Anaemia and Women
Living with low hemoglobin, often referred to as anemia, can significantly impact women's health and daily life. While the condition can be challenging, but with proper management strategies, women can improve their quality of life. By incorporating a balanced diet, supplements as advised, exercise, adequate rest, and seeking medical guidance, women can effectively navigate and cope with the challenges posed by low hemoglobin levels.
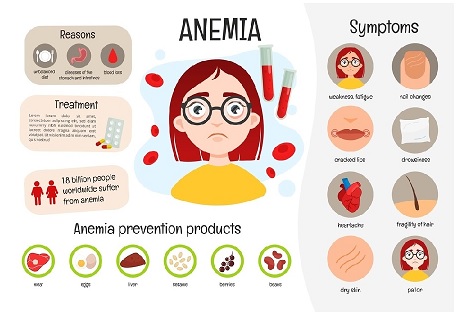
Understanding anaemia
Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. When levels are low, it can lead to fatigue, weakness, and other health challenges, especially in women.For many women, anemia is a common issue, often due to various reasons such as menstrual bleeding, pregnancy, nutritional deficiencies, or chronic diseases. Coping with low hemoglobin levels can be challenging, but there are ways to manage it effectively.
Fatigue and weakness are among the primary symptoms of low hemoglobin. This can make everyday tasks feel exhausting and can impact productivity. Simple activities that were once effortless may suddenly seem daunting. However, with proper management, these challenges can be alleviated.
How you can improve your hemoglobin levels?
Diet plays a crucial role in managing low hemoglobin levels. Consuming iron-rich foods such as leafy greens, red meat, beans, and fortified cereals can help increase iron intake, thus boosting hemoglobin production. Pairing these foods with sources of vitamin C can enhance iron absorption in the body.
Supplements prescribed by healthcare professionals can also aid in raising hemoglobin levels. Iron supplements are commonly recommended for those with anemia, but it's essential to consult a doctor before starting any new supplements as excessive iron can have adverse effects.
Moreover, lifestyle adjustments can make a significant difference. Regular exercise, although initially tiring, can gradually improve stamina and energy levels. Adequate rest and sleep are equally important in managing fatigue associated with low hemoglobin.
For women dealing with heavy menstrual bleeding, seeking medical advice and exploring treatment options can help manage and reduce blood loss. Similarly, during pregnancy, prenatal care and monitoring hemoglobin levels are vital for both maternal and fetal health.
Support from friends, family, or support groups can also make a difference. Sharing experiences and seeking advice or encouragement from others who have dealt with similar health issues can provide emotional support and valuable insights into coping mechanisms.
Regular check-ups and communication with healthcare providers are crucial for managing low hemoglobin levels. Periodic blood tests help monitor hemoglobin and iron levels, allowing for timely interventions or adjustments to treatment plans as needed.
